RICE
Rice is the seed of the grass species Oryza sativa (Asian rice) or Oryza glaberrima (African rice). As a cereal grain, it is the most widely consumed staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in Asia. It is the agricultural commodity with the third-highest worldwide production (rice, 741.5 million tonnes in 2014), after sugarcane (1.9 billion tonnes) and maize (1.0 billion tonnes).
Since sizable portions of sugarcane and maize crops are used for purposes other than human consumption, rice is the most important grain with regard to human nutrition and caloric intake, providing more than one-fifth of the calories consumed worldwide by humans.There are many varieties of rice and culinary preferences tend to vary regionally.
Rice, a monocot, is normally grown as an annual plant, although in tropical areas it can survive as a perennial and can produce a ratoon crop for up to 30 years. Rice cultivation is well-suited to countries and regions with low labor costs and high rainfall, as it is labor-intensive to cultivate and requires ample water. However, rice can be grown practically anywhere, even on a steep hill or mountain area with the use of water-controlling terrace systems. Although its parent species are native to Asia and certain parts of Africa, centuries of trade and exportation have made it commonplace in many cultures worldwide.
The traditional method for cultivating rice is flooding the fields while, or after, setting the young seedlings. This simple method requires sound planning and servicing of the water damming and channeling, but reduces the growth of less robust weed and pest plants that have no submerged growth state, and deters vermin. While flooding is not mandatory for the cultivation of rice, all other methods of irrigation require higher effort in weed and pest control during growth periods and a different approach for fertilizing the soil.
The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera Zizania and Porteresia, both wild and domesticated, although the term may also be used for primitive or uncultivated varieties of Oryza.
Etymology
First used in English in the middle of the 13th century, the word "rice" derives from the Old French ris, which comes from Italian riso, in turn from the Latin oriza, which derives from the Greek ὄρυζα (oruza). The Greek word is the source of all European words (cf. Welsh reis, German Reis, Lithuanian ryžiai, Serbo-Croatian riža, Polish ryż, Dutch rijst, Hungarian rizs, Romanian orez).
The origin of the Greek word is unclear. It is sometimes held to be from the Tamil word (arisi), or rather Old Tamil arici. However, Krishnamurti disagrees with the notion that Old Tamil arici is the source of the Greek term, and proposes that it was borrowed from descendants of Proto-Dravidian *wariñci instead. Mayrhofer suggests that the immediate source of the Greek word is to be sought in Old Iranian words of the types *vrīz- or *vrinj- (Source of the modern Persian word Berenj), but these are ultimately traced back to Indo-Aryan (as in Sanskrit vrīhí-) and subsequently to Dravidian.
Characteristics
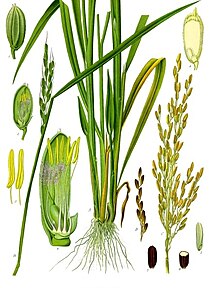
The rice plant can grow to 1–1.8 m (3.3–5.9 ft) tall, occasionally more depending on the variety and soil fertility. It has long, slender leaves 50–100 cm (20–39 in) long and 2–2.5 cm (0.79–0.98 in) broad. The small wind-pollinated flowers are produced in a branched arching to pendulous inflorescence 30–50 cm (12–20 in) long. The edible seed is a grain (caryopsis) 5–12 mm (0.20–0.47 in) long and 2–3 mm (0.079–0.118 in) thick.



No comments:
Post a Comment